Удельный вес: Жидкости, газы и твердые тела
Specific Gravities of Liquids
|
Liquids and Fluids |
(oC) |
SG |
|
1Propanol |
20 |
0.805 |
|
2Propanol |
20 |
0.786 |
|
Acetic Acid |
25 |
1.052 |
|
Acetone |
25 |
0.787 |
|
Acetylene, liquid |
121oF |
0.62 |
|
Acetylene, liquid |
70oF |
0.38 |
|
Alcohol, ethyl (ethanol) |
25 |
0.787 |
|
Alcohol, methyl (methanol) |
25 |
0.791 |
|
Beer |
25 |
1.01 |
|
Benzene |
25 |
0.876 |
|
Benzil |
25 |
1.054 |
|
Butane, liquid |
25 |
0.601 |
|
Butylamine |
20 |
0.742 |
|
Caproic acid |
25 |
0.924 |
|
Carbolic acid |
15 |
0.959 |
|
Carbon disulfide |
25 |
1.265 |
|
Carbon tetrachloride |
25 |
1.589 |
|
Chloride |
25 |
1.56 |
|
Chlorine |
60oF |
1.42 |
|
Chlorodifluoromethane refrigerant R22 |
25 |
1.197 |
|
Citric acid |
25 |
1.665 |
|
Coconut Oil |
15 |
0.925 |
|
Crude oil, California |
60oF |
0.918 |
|
Decane |
25 |
0.728 |
|
Ethane |
89 |
0.572 |
|
Ethanol |
20 |
0.789 |
|
Ether (Diethyl ether) |
25 |
0.716 |
|
Ethyl acetate |
20 |
0.901 |
|
Ethylamine |
16 |
0.683 |
|
Ethylene glycol |
25 |
1.100 |
|
Formaldehyde |
45 |
0.815 |
|
Fuel oil |
60oF |
0.893 |
|
Gasoline, natural |
60oF |
0.713 |
|
Gasoline, Vehicle |
60oF |
0.739 |
|
Glycol |
25 |
1.11 |
|
Heptane |
25 |
0.681 |
|
Linseed Oil |
25 |
0.932 |
|
mXylene |
20 |
0.864 |
|
Mercury |
25 |
13.633 |
|
Methane |
164 |
0.466 |
|
Methanol |
20 |
0.791 |
|
Methyl acetate |
20 |
0.935 |
|
Milk |
1.035 |
|
|
Naphtha, Petroleum Naphtha |
15 |
0.667 |
|
Nonanol |
25 |
0.823 |
|
oXylene |
20 |
0.880 |
|
Octane |
25 |
0.701 |
|
Oil, Castor |
25 |
0.959 |
|
Olive Oil |
15 |
0.915 |
|
Oxygen |
183 |
1.14 |
|
pXylene |
20 |
0.861 |
|
Palm Oil |
15.5 |
0.923 |
|
Palmitic Acid |
25 |
0.853 |
|
Propane |
40 |
0.585 |
|
Propane |
25 |
0.495 |
|
Propyl acetate |
20 |
0.889 |
|
Sea water |
25 |
1.028 |
|
Trichlorofluoromethane refrigerant R11 |
25 |
1.480 |
|
Turpentine |
25 |
0.871 |
|
Water, pure |
39.2oF (4oC) |
1.000 |
|
Water, sea |
77oF |
1.025 |
Specific Gravities of Gases
|
Gases |
|
|
Acetylene (ethyne) |
0.899 |
|
Air |
1.000 |
|
Alcohol vapor |
1.601 |
|
Ammonia |
0.59 |
|
Argon |
1.38 |
|
Benzene |
2.6969 |
|
Blast Furnace gas |
1.02 |
|
Carbon dioxide |
1.5189 |
|
Chlorine |
2.486 |
|
Coke Oven Gas |
0.44 |
|
n Decane |
4.9125 |
|
Deutrium D2 |
0.070 |
|
Ethane |
1.0378 |
|
Ether vapor |
2.586 |
|
Ethylbenzene |
3.6655 |
|
Ethylene (Ethene) |
0.9686 |
|
3 Ethylpentane |
3.4596 |
|
Fluorine |
1.31 |
|
Helium He |
0.138 |
|
Hydrogen |
0.0696 |
|
Hydrogen chloride |
1.268 |
|
Hydrogen sulfide |
1.1763 |
|
Hydrofluoric acid |
2.370 |
|
Isobutene |
1.9372 |
|
Isooctane |
3.9439 |
|
Krypton |
2.89 |
|
Marsh gas |
0.555 |
|
Mercury vapor |
6.940 |
|
Methane |
0.5537 |
|
Natural Gas (typical) |
0.60 0.70 |
|
Neon |
0.697 |
|
Nitric oxide |
1.037 |
|
Nitrogen (pure) |
0.9669 |
|
Nitrogen (atmospheric) |
0.9723 |
|
Oxygen |
1.1044 |
|
Ozone |
1.660 |
|
Sulfur Dioxide |
2.264 |
|
Water vapor |
0.6218 |
|
Xenon |
4.53 |
Specific Gravities of Solids
|
Solids and Metals |
|
|
ABS, extrusion grade |
1.05 |
|
Acrylic |
1.19 |
|
3.4 |
|
|
Antimony |
6.69 |
|
Asphalt |
1.1 |
|
Bark |
0.25 |
|
Barite |
4.5 |
|
Barium |
3.62 |
|
1.848 |
|
|
Bismuth |
9.79 |
|
Boron |
2.32 |
|
Brass, cast rolled |
8.4 8.7 |
|
Brick, common red |
1.75 |
|
Brick, fire clay (firebrick) |
2.4 |
|
Calcium |
4.58 |
|
Carbon, solid |
2.1 |
|
Carbon, powdered |
0.08 |
|
Cement |
1.2 1.5 |
|
Cerium |
6.77 |
|
Chalk |
2.3 |
|
Charcoal, wood |
0.4 |
|
Chromium |
7.19 |
|
Cobalt |
8.71 |
|
Copper |
8.89 |
|
Diamond |
3.51 |
|
Earth, dry |
1.4 |
|
Epoxy |
1.8 |
|
Europium |
5.244 |
|
Ferrosilicon 15% |
6.7 7.1 |
|
Gallium |
5.91 |
|
Glass min. |
2.4 |
|
Glass max. |
2.8 |
|
19.32 |
|
|
2.07 |
|
|
13.31 |
|
|
Ice (0oC, 32oF) |
0.92 |
|
7.31 |
|
|
Iodine |
4.93 |
|
Iron cast min. |
7.03 |
|
Iron cast max. |
7.13 |
|
11.35 |
|
|
Leather |
0.95 |
|
Limestone |
2.6 |
|
0.53 |
|
|
Magnesite |
3 |
|
Manganese |
7.21 7.44 |
|
Magnesium |
1.738 |
|
Mercury |
13.534 |
|
10.22 |
|
|
7.00 |
|
|
Nickel |
8.90 |
|
Nylon 6 Cast |
1.16 |
|
Paper |
0.9 |
|
12.02 |
|
|
Phosphorus |
1.8 |
|
Plaster, light |
0.7 |
|
Platinum |
21.45 |
|
Porcelain |
2.5 |
|
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
2.19 |
|
PVC |
1.39 |
|
Rhenium |
21.02 |
|
Silicon |
2.33 |
|
3.1 |
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
Tile |
1.8 |
|
Tin |
7.31 |
|
19.22 |
|
|
Tungsten carbide |
14.29 |
|
Wood, oak |
0.7 |
|
Zinc, cast rolled |
6.9 7.2 |
|
6.506 |
Specific Gravity: FAQs
1. What is specific gravity?
Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance (typically water) at a specific temperature and pressure. It's a dimensionless quantity often used to determine the relative density of liquids and solids compared to water.
2. How is the specific gravity calculated?
Specific gravity is calculated by dividing the density of a substance by the density of the reference substance (usually water). The formula is:
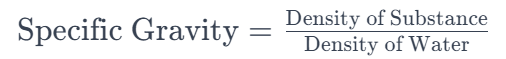
3. Why is specific gravity important?
l Density Comparison: It helps compare the density of a substance to that of water, giving an indication of its buoyancy or sinking behavior.
l Material Properties: Specific gravity is crucial in various fields like metallurgy, construction, and chemistry to assess material properties and behavior.
4. What does a specific gravity value tell us?
A specific gravity of less than 1 indicates that the substance is less dense than water and will float on water.
A specific gravity greater than 1 indicates that the substance is denser than water and will sink.
5. Can specific gravity change?
Yes. Specific gravity can change with temperature, pressure, and the state of matter (solid, liquid, gas). For example, substances expand or contract with temperature changes, altering their density and, consequently, their specific gravity.
6. How is specific gravity used in different industries?
l Brewing: Determines sugar content in beer by measuring specific gravity before and after fermentation.
l Mining and Metallurgy: Assesses ore quality and determines the concentration of minerals.
l Construction: Evaluates the strength and quality of materials like concrete and aggregates.
7. How is the specific gravity measured?
l Hydrometer: Used for liquids, it measures the density of a liquid and calculates specific gravity.
l Pycnometer: Measures the volume of solids and liquids to determine density and specific gravity.
l Archimedes' Principle: Measures the volume of irregularly shaped solids immersed in a liquid to determine their density and specific gravity.
8. Are there any limitations to using specific gravity?
Specific gravity is a valuable indicator but has limitations. It doesn't provide detailed information about a substance's composition or properties beyond density. Additionally, it assumes standard conditions (temperature, pressure) for accurate comparison.

 Бары
Бары
 Бисер и шары
Бисер и шары
 Болты и гайки
Болты и гайки
 Кристаллы
Кристаллы
 Диски
Диски
 Волокна и ткани
Волокна и ткани
 Фильмы
Фильмы
 Хлопья
Хлопья
 Пены
Пены
 Фольга
Фольга
 Гранулы
Гранулы
 Медовые соты
Медовые соты
 Чернила
Чернила
 Ламинат
Ламинат
 Шишки
Шишки
 Сетки
Сетки
 Металлизированная пленка
Металлизированная пленка
 Тарелка
Тарелка
 Порошки
Порошки
 Род
Род
 Простыни
Простыни
 Одиночные кристаллы
Одиночные кристаллы
 Мишень для напыления
Мишень для напыления
 Трубки
Трубки
 Стиральная машина
Стиральная машина
 Провода
Провода
 Конвертеры и калькуляторы
Конвертеры и калькуляторы




 Chin Trento
Chin Trento



